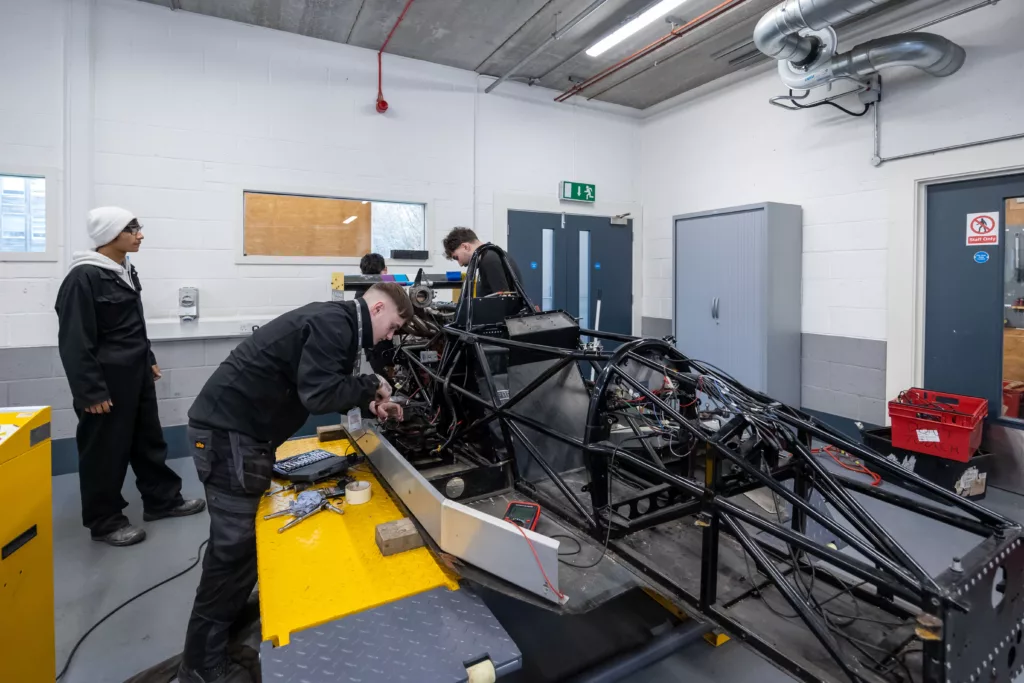
Employing an Engineering apprentice
Engineering touches so many industries and businesses, and with the rate of developments in technology, employing an engineering apprentice can be a great way to stay ahead of the game and keep up to date with the latest developments.
Employing an Apprentice: The Benefits
As well as offering a fresh perspective, engineering apprentices have the opportunity to develop their skills on the job and through a collaborative learning experience between college and employer, they will learn from industry experts, get to understand the latest technology and theories, and network and share ideas with other apprentices from other industries. But with so many options, how do you go about finding the right apprentice for your business? Here is our guide to the current engineering standards and what they offer your business.
Level 2 Engineering Operative
Working individually or as part of a team, an engineering operative may be involved in a range of engineering operations. For example, ensuring machines and equipment used are maintained and serviceable, dealing with breakdowns, restoring components and systems to serviceable condition, operating a variety of machines, assembling and repairing machines, press tools, dies, jigs, fixtures and other tools.
Level 3 Composites Technician
Composites manufacturing is the combining of materials to form a lighter and stronger alternative to metal. A composites technician will engage in a variety of processes in the production of these materials. Their specialist knowledge and skills may be deployed in the areas of design, tooling, moulding, lay-up, curing, machining, inspection, testing, repairing and material production.

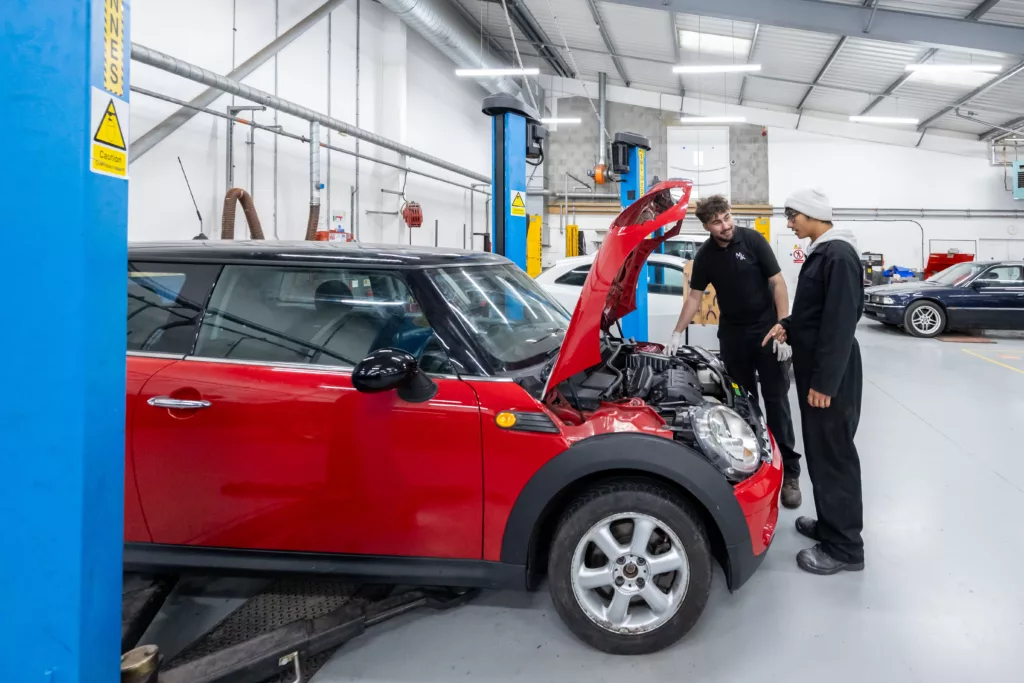
Level 3 Design and Draughtsperson
As an engineering design and draughtsperson, the primary role will be to produce designs and drawings. As such, the apprentice will understand and create their own technical drawings and specifications; produce CAD (Computer Aided Design) models and engineering drawings; identify factors likely to affect design decisions and be able to communicate design information to internal and external parties.
Level 3 Engineering Fitter
Generally speaking, an engineering fitter will be involved in the production of complex, high-value, low-volume components or assemblies. They may have a mechanical, electrical, electronic, control systems, pipe fitting or instrumentation bias. Regardless of their bias, all engineering fitters will need to interpret drawings/specifications and be able to plan their work to ensure they have the right tools, equipment and resources. By doing these things and using their knowledge and skills, an engineering fitter will be able to complete their tasks to the required specification and against the required quality standards.
Level 3 Machinist
A machinist will be involved in highly-skilled, complex and precision work, machining components from specialist materials using conventional and/or CNC machine tools such as lathes, mills, and multi-axis CNC machines. Apprentices will learn how to set up, operate, adjust/edit equipment and produce, prove and edit CNC programmes whilst working with their employer.

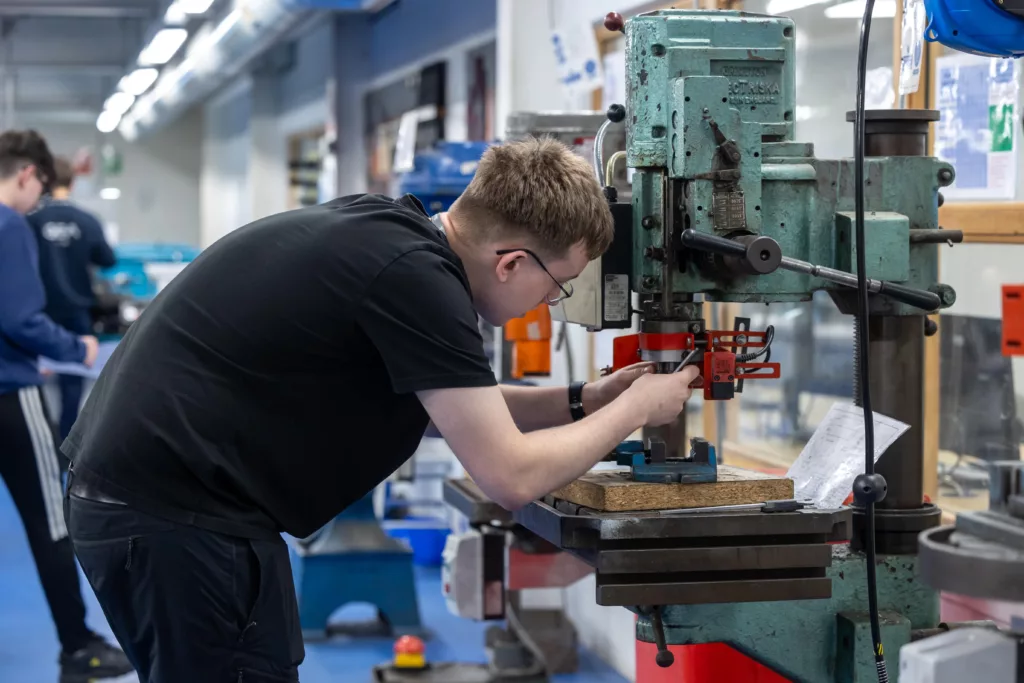
Level 3 Mechatronics
A mechatronics maintenance engineer will be involved in a broad range of activities that are designed to ensure that plant and equipment perform to the required standard. Activities may include installation, testing, fault-finding and planned maintenance of complex automated equipment. As such, a mechatronics maintenance technician will have a broad range of knowledge and skills covering electrical, electronic, mechanical, fluid power and control systems disciplines.
Level 3 Product Design and Development
Product Design & Development Technicians primarily work on all stages of product creation and modification. Product and design technicians support activities ranging from early concept feasibility, design and development stages right through to final preparation for launch and customers. This includes working in concept studios, rapid prototyping, assembly, testing, validating and analysing performance. Apprentices will work closely with engineers in bringing new concepts to life or supporting redesigns of existing products.
Level 3 Toolmaker and Tool and Die Maintenance
A Toolmaker and Tool & Die Maintenance Technician will predominantly be involved in the highly-skilled, complex and specialist detailed work of manufacturing and maintaining the engineering tooling used to produce components, products and assemblies. It involves a broad range of activities, including the interpretation of engineering drawings and technical instructions, the use of hand, machine and automated computer-controlled machine tools and measuring equipment.

Level 3 Technical Support
Technical Support Technicians work as part of a team to provide technical support and expertise for all areas of the Engineering and Manufacturing function. As part of the role, apprentices may be involved with production scheduling/planning, process control, performance and continuous improvement techniques, quality control and inspection. Apprentices will be able to work with minimum supervision and take responsibility for the quality, accuracy and timely delivery of their work.
Level 4 Propulsion Technician
Propulsion Technicians are responsible for the testing of building functions that support the development of propulsion systems such as internal combustion engines, hybrid and electric propulsion technology and advanced control systems. A propulsion technician will carry out a range of specialist tasks to develop, improve or create new propulsion technologies. They will take a proactive role in development, build or test delivery, taking responsibility for creating, editing, first-line data analysis and quality validation.
If you have any questions about engineering apprenticeships and how they could benefit your business, you can find more information and details on how to get in touch with us.